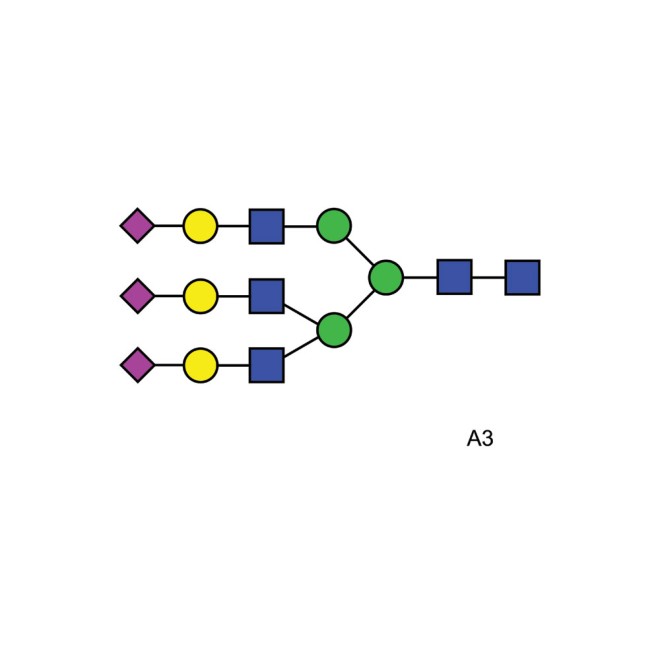
A3 glycan (A3G3S3)
Triantennary N-glycan that contains terminal sialic acid residues. m/z: 2879.0106
Tri-sialylated, tri-antennary complex-type N-glycan (oligosaccharide). The product supplied is a mixture of isomers differing in the type of sialic acid linkages (Neu5Acα2-3 or Neu5Acα2-6) and the Gal residue linkage of one of the arms (Galβ1-4 or Galβ1-3).
Product Specification
A3 Glycan Synonyms: A3 N-linked oligosaccharide, A3G3S3
Description: Tri-sialylated, tri-antennary complex-type N-glycan (oligosaccharide). The product supplied is a mixture of isomers differing in the type of sialic acid linkages (Neu5Acα2-3 or Neu5Acα2-6) and the Gal residue linkage of one of the arms (Galβ1-4 or Galβ1-3).
Molecular Weight: 2879
Purity: > 90% pure as assessed by a combination of 1 H-NMR and HPLC.
Sources: A3 glycans are found on several mammalian glycoproteins including bovine serum fetuin (bSF). This product is typically purified from the oligosaccharide pool released from bSF by hydrazinolysis using a combination of HPLC and glycosidase digestion.
Form: Dry. Dried by centrifugal evaporation from an aqueous solution containing approximately 50 mmol dm-3 of ammonium acetate (added to minimize acid-catalysed desialylation).
Storage: -20˚C both before and after dissolution. This product is stable for at least 5 years as supplied.
Shipping: The product can be shipped at ambient when dry. After dissolution, ship on dry ice.
Handling: Allow the unopened vial to reach ambient temperature and tap unopened on a solid surface to ensure that most of the lyophilized material is at the bottom of the vial. Gently remove the cap, add the desired volume of reconstitution medium, re-cap and mix thoroughly to bring all the oligosaccharide into solution. For maximal recovery of oligosaccharide, ensure that the cap lining is also rinsed and centrifuge the reconstituted vial briefly before use. Ensure that any glass, plasticware or solvents used are free of glycosidases and environmental carbohydrates. Minimise exposure to elevated temperatures or extremes of pH. High temperatures and low pH will cause desialylation. High pH will cause epimerisation of the reducing terminus GlcNAc.
Safety: This product is non-hazardous and has been purified from natural sources certified to be free of all hazardous material including pathogenic biological agents.
HPLC Analysis of Glycans
LudgerPure unlabeled glycans and LudgerTag labeled glycans may be separated and analysed by a variety of HPLC (high pressure liquid chromatography) methods using LudgerSep™ HPLC columns.
The LudgerSep columns are are available for the following applications:
Separation of charged and neutral glycans via anion exchange columns:
LS-C3-7.5×75 LudgerSep C3 – 7.5x75mm
LS-C2-4.6×50 LudgerSep C2 – 4.6x50mm
LS-C-BUFFX4 LudgerSep C Buffer
Profile analysis of neutral and charged glycans via normal phase columns:
LS-N2-2.0×250 LudgerSep N2 – 2.00x250mm
LS-N2-4.6×250 LudgerSep N2 – 4.6x250mm
LS-N1-4.6×250 LudgerSep N1
The LudgerSep N2 columns are an especially powerful tool for the purification and analysis of LudgerTag labeled oligosaccharides from complex glycan mixtures. Please contact us for advise regarding your particular application.
Mass Spectrometry and Electrophoresis
LudgerPure and LudgerTag labeled glycans may also be analysed by mass spectrometry, electrophoresis, and various types of spectroscopy. Please call us for advice on the dyes and analysis conditions most suitable for your intended analyses.


-660x660.jpg)
