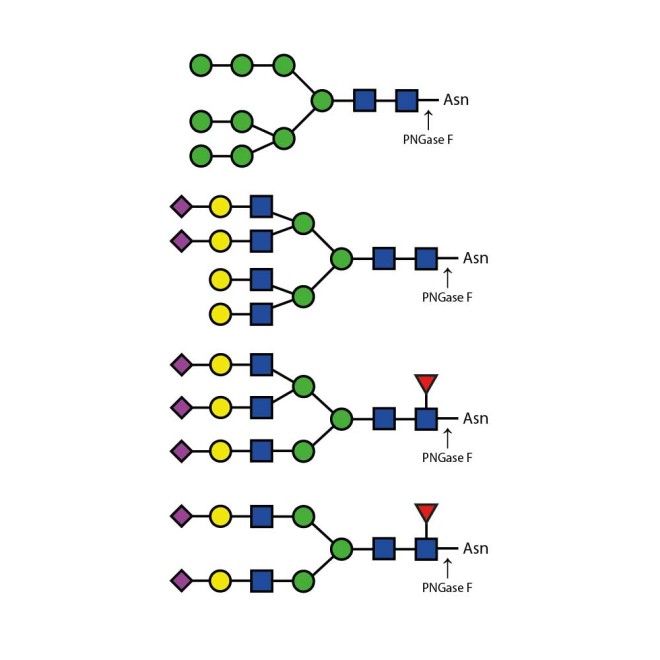
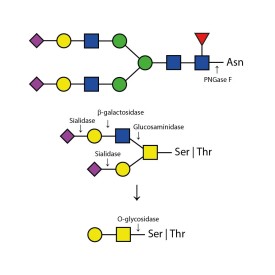
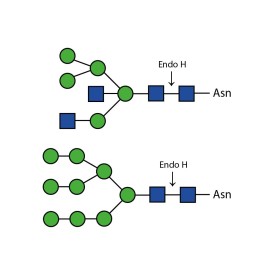
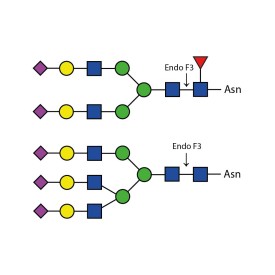
PNGase F (Peptide-N-Glycosidase F)
References:
1. Bayer, E.A., F. De Meester, T. Kulik and M. Wilchek. Preparation of deglycosylated egg white avidin. Appl Biochem Biotech 53: 1-9 (1995)
2. Elder, J.H. and S. Alexander. endo-b-N-Acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 4540-4544 (1982)
3. Tarentino, A .L., C.M. Gomez and T.H. Plummer, Jr. Deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans by peptide :N-glycosidase F. Biochemistry 24: 4665-4671 (1985)
4. Tarentino A.L. and T.H. Plummer. Enzymatic deglycosylation of asparagine -linked glycans: purification, properties, and specificity of oligosaccharide-cleaving enzymes from Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Meth Enzymol 230: 44-57 (1994)
5. Trimble R.B. and A.L. Tarentino. Identification of distinct endoglycosidase (endo) activities in Flavobacterium meningosepticum: endo F1 , endo F2 and endo F3. Endo F1 and endo H hydrolyze only high mannose and hybrid glycans. J Biol Chem 266: 1646-1 651 (1991)
6. Taga, E. M., A. Waheed and R. L. Van Etten. Structural and chemical characterization of a homogeneous peptide-N-glycosidase from almond. Biochemistry 23: 815-22 (1984)
7. Tarentino AL, Trimble RB, Plummer TH. Enzymatic approaches for studying the structure, synthesis, and processing of glycoproteins. Methods in Cell Biology: 32: 111-39 (1989)
8. Anthony L. , Tarentino and Thomas H. Plummer Jr. Enzymatic deglycosylation of asparagine-linked glycans: Purification, properties, and specificity of oligosaccharide-cleaving enzymes from Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Methods in Enzymology: 230: 44-57. (1994)
9. Tarentino AL, Plummer TH. Oligosaccharide accessibility to peptide:N-glycosidase as promoted by protein-unfolding reagents. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 257 (18): 10776-80. (1982)
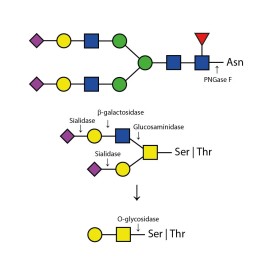
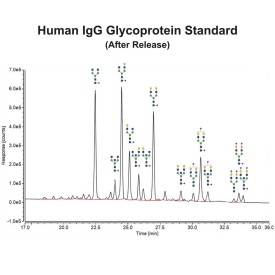
PNGase F is suitable for the release of all types (high-mannose, hybrid and complex) N-linked glycans from glycoproteins and glycopeptides. PNGase F will not remove oligosaccharides containing α(1-3) linked core fucose commonly found on plant glycoproteins.
PNGase F cleaves N-linked (asparagine-linked) oligosaccharides from glycoproteins. The enzyme deaminates asparagine to aspartic acid, leaving the oligosaccharides intact. Denaturation increases the rate of cleavage. Most native proteins can still be completely N-deglycosylated but incubation time must be increased. The enzyme will remain fully active under reaction conditions (37°C) for at least 96 hours. PNGase F will not remove oligosaccharides containing Alpha-(1,3)-linked core fucose commonly found on plant glycoproteins; for this purpose, use peptide N-glycosidase A.
Product specifications:
PNGase F cleaves N-linked (asparagine-linked) oligosaccharides from glycoproteins. The enzyme deaminates asparagine to aspartic acid, leaving the oligosaccharides intact. PNGase F will not remove oligosaccharides containing Alpha-(1,3)-linked core fucose commonly found on plant glycoproteins; for this purpose, use peptide N-glycosidase A.
Denaturation increases the rate of cleavage. Most native proteins can still be completely N-deglycosylated but incubation time may need to be increased. The enzyme will remain fully active under reaction conditions (37˚C) for at least 96 hours.
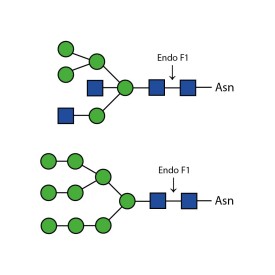
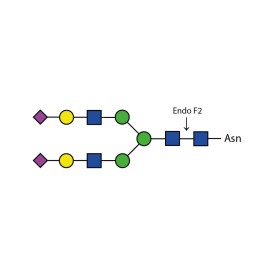
There are a number of alternative enzymes which can be used to remove N-glycans, most especially the Endo F family of enzymes and Endo H. These enzymes cleave between the two N-acetylglucosamine residues in the core of the oligosaccharide, generating a truncated sugar molecule with one N-acetylglucosamine residue remaining on the asparagine. This leaves a charged sugar which can assist in keeping proteins in solution that precipitate after deglycosylation with PNGase F which removes the oligosaccharide intact. Endo F1 cleaves high mannose and some hybrid type N-glycans. Endo F2 will removes biantennary and high mannose (at a 40X reduced rate). Endo F3 releases of triantennarry and fucosylated biantennary N-glycans. Endo H removes hybrid or high mannose glycans.
Source: Elizabethkingia miricola (was Chryseobacterium meningosepticum)
EC: 3.5.1.52 PDB 1PGS UniProt Q9XBM8
Alternative Names: PNGase F, Peptide N Glycosidase F, N-Glycosidase, N-Glycanase
Contents E-PNG01:
PNGase F in 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 - 60µL
5x Reaction Buffer 7.5 – 250 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.5
Denaturation Solution – 2% SDS, 1 M Beta-mercaptoethanol
Triton X-100 – 15% solution
Contents E-PNG01-200 (enzyme only):
PNGase F in 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 - 200µL
Specific Activity: >25 U/mg
Activity: 5 U/mL
Molecular weight: 36,000 daltons
pH range: 6-10, optimum 7.5
Protocol:
1. Add up to 200 µg of glycoprotein to an Eppendorf tube. Adjust to 35 µL final volume with de-ionized water.
2. Add 10 µL 5x Reaction Buffer 7.5 and 2.5 µL of Denaturation Solution. Heat at 100°C for 5 minutes.
3. Cool. Add 2.5 µL of Triton X-100 and mix.
4. Add 2.0 µL of enzyme to the reaction. Incubate 3 hours at 37°C.
Specificity: Cleaves all asparagine-linked complex, hybrid or high mannose oligosaccharides unless alpha(1-3) core fucosylated; asparagine must be peptide bonded at both termini, Endo F free
Specific Activity: Defined as the amount of enzyme required to catalyze the release of N-linked oligosaccharides from 1 micromole of denatured RNase B in 1 minute at 37°C, pH 7.5. Cleavage is monitored by SDS-PAGE (cleaved RNase B migrates faster).
Storage: Store enzyme at 4°C.