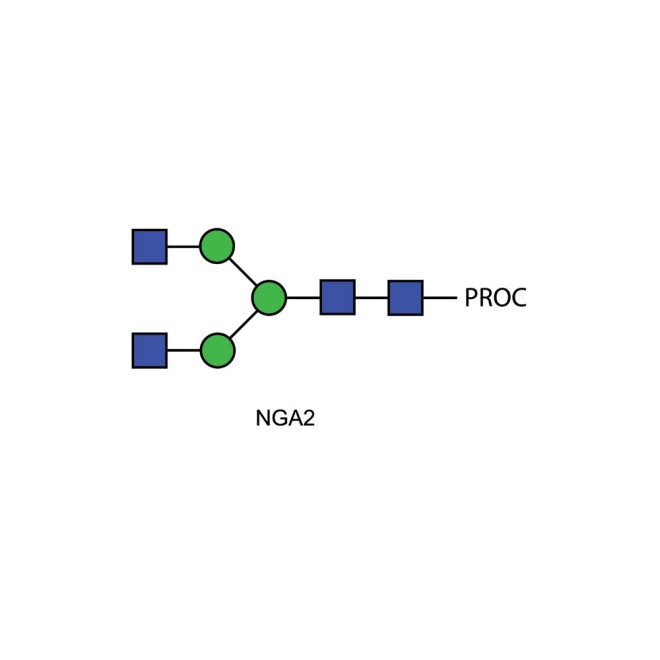
NGA2 glycan (A2), procainamide labelled
References
Kozak RP, Tortosa CB, Fernandes DL, Spencer DI Comparison of procainamide and 2-aminobenzamide labeling for profiling and identification of glycans by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection coupled to electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry Anal Biochem. Oct 1;486:38-40 (2015)
Klapoetke S, Zhang J, Becht S, Gu X, Ding X, The evaluation of a novel approach for the profiling and identification of N-linked glycan with a procainamide tag by HPLC with fluorescent and mass spectrometric detection, J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 53 (2010) 315–324.
Lei Zhang, Shen Luo, and Baolin Zhang Glycan analysis of therapeutic glycoproteins MABS 2016, VOL. 8, NO. 2, 205–215
Crescioli S, Chiaruttini G, Mele S, Ilieva KM, Pellizzari G, Spencer DIR, Gardner RA, Lacy KE, Spicer JF, Tutt ANJ, Wagner GK, Karagiannis SN Engineering and stable production of recombinant IgE for cancer immunotherapy and AllergoOncology Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology Jan 31. pii: S0091-6749(18)30081-2 (2018)
Thomson RI, Gardner RA, Strohfeldt K, Fernandes DL, Stafford GP, Spencer DIR, Osborn HMI Analysis of Three Epoetin Alpha Products by LC and LC-MS Indicates Differences in Glycosylation Critical Quality Attributes, Including Sialic Acid Analytical Chemistry Content Jun 20;89(12):6455-6462 (2017)
Procainamide labelled asialo, agalacto biantennary oligosaccharide
Biantennary N-glycan that contains terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues, 20pmol.
m/z: 1535.6565
Product Specification
NGA2 Procainamide Glycan Synonyms: NGA2 N-linked oligosaccharide. G0, A2
LudgerTag procainamide labeled glycans can be analyzed by UHPLC, HPLC, ESI-MS, and LC-ESI-MS methods. Because of its improved ionization efficiency compared to 2-AB labeling it can permit identification of minor glycans (<1% relative peak area) by ESI-MS.
Description: Asialo- agalacto- bi-antennary complex-type N-glycan (oligosaccharide).
Sources: NGA2 glycan is found on many mammalian glycoproteins including IgG, gamma globulins, and many serum glycoproteins. This product is typically purified from the oligosaccharide pool released from bovine serum by hydrazinolysis using a combination of HPLC and glycosidase digestion.
Form: Dry. Dried by centrifugal evaporation from an aqueous solution.
Molecular Weight: 1536
Mass free dye: 235.33
Mass Added to Glycan: 219.172
Fluorescence: λex = 310 nm, λem = 370 nm.
Amount: 20 pmols
Purity: >90% pure as assessed by a combination of 1 H-NMR and HPLC.
Storage: -20˚C both before and after dissolution. This product is stable for at least 5 years as supplied.
Shipping: The product can be shipped at ambient when dry. After dissolution, ship on dry ice.
Handling: Allow the unopened vial to reach ambient temperature and tap unopened on a solid surface to ensure that most of the lyophilized material is at the bottom of the vial. Gently remove the cap, add the desired volume of reconstitution medium, re-cap and mix thoroughly to bring all the oligosaccharide into solution. For maximal recovery of oligosaccharide, ensure that the cap lining is also rinsed and centrifuge the reconstituted vial briefly before use. Ensure that any glass, plasticware or solvents used are free of glycosidases and environmental carbohydrates. Minimise exposure to elevated temperatures or extremes of pH. High temperatures and low pH will cause desialylation. High pH will cause epimerisation of the reducing terminus GlcNAc.
Safety: This product is non-hazardous and has been purified from natural sources certified to be free of all hazardous material including pathogenic biological agents.
HPLC Analysis of the NGA2 Procainamide Glycan
Fluorescence response Procainamide glycans show a much higher sensitivity as compared to 2-AB labeled glycans, providing peak heights three times higher than traditional 2-AB labeled glycans. The procainamide labeled sugars show comparable separation to HILIC-UHPLC assays with 2-AB.
Mass Spectrometry and Electrophoresis
Mass spectrometry response Due to its high ionization efficiency, procainamide shows much higher sensitivities the seen with 2-AB. When analyzed using ESI-MS and ESI-MS/MS, procainamide produces twenty-two times higher peaks than 2-AB. This provides a great platform for the detection and identification on minor peaks by MS/MS analysis..


-660x660.jpg)
